Explosion Testing for dust, gases & vapours


© January 2026
1m
3
Explosion indices test (K
st
& P
max
)
Testing in larger volume vessels
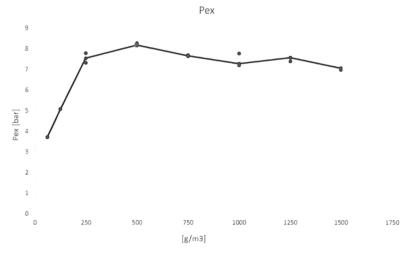
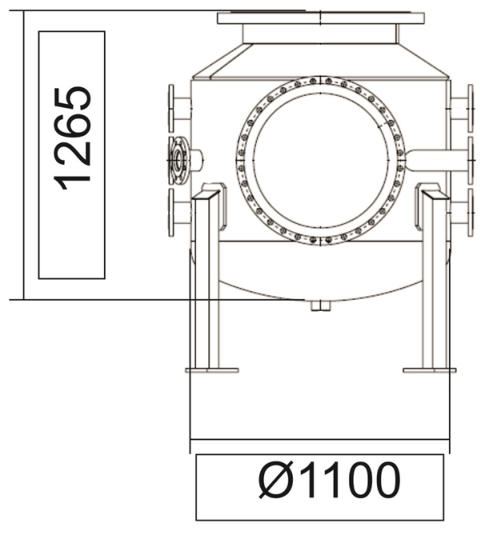
Kst value and Pmax may also be measured in the laboratory’s 1m 3 test vessel. Testing at larger scale has the advantage of accommodating coarser and more fibrous materials that may hinder proper dispersion in the 20 litre sphere. However, the time to test each dust concentration and sample preparation (if needed) takes significantly longer and overall the price is higher than the equivalent 20 litre sphere test. Price on application - please email for details. The same test standards are used, namely EN 14034-1 (determination of the maximum explosion pressure Pmax of dust clouds), EN 14034-2 (determination of the maximum rate of explosion pressure rise of dust clouds Kst), EN ISO/IEC 80079- 20-2 and with the option of testing to ASTM E1226. Explosive atmosphere is produced by injecting the sample under test through a spherical nozzle. The flammable dust is placed into a dust agitator having a volume of 5.4 litres, which is pressurized to 20 bar. It is opened using an electro-pneumatic quick release valve. Two pyrotechnic initiators are used, each having a value of 5 kJ, which are placed in the centre of the explosion vessel. The 1m 3 test vessel has a H/D ratio of 1,15, static pressure resistance of 16 bar and maximum dynamic test pressure of 23 bar. The ST class is based on the Kst value as follows: ST class 0 - Kst value = 0 ST class 1 - Kst value less than 200 bar m/sec ST class 2 - Kst value between 200 and 300 bar m/sec ST class 3 - Kst value greater than 300 bar m/sec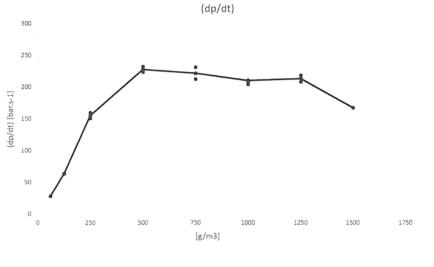


- Classification test
- Explosion indices test
- 1m3 explosion test
- Minimum ignition energy
- Minimum ignition temperature
- Layer ignition temperature
- Limiting oxygen concentration
- Lower explosible limit
- Isothermal basket test
- Powder volume resistivity
- Train fire
- Thermal screen
- Air Over Layer
- UN Classification testing
Explosion Testing


© January 2026
1m
3
Explosion
indices test (K
st
&
P
max
)
Testing in larger volume vessels
Kst value and Pmax may also be measured in the laboratory’s 1m 3 test vessel. Testing at larger scale has the advantage of accommodating coarser and more fibrous materials that may hinder proper dispersion in the 20 litre sphere. However, the time to test each dust concentration and sample preparation (if needed) takes significantly longer and overall the price is higher than the equivalent 20 litre sphere test. Price on application - please email for details. The same test standards are used, namely EN 14034-1 (determination of the maximum explosion pressure Pmax of dust clouds), EN 14034-2 (determination of the maximum rate of explosion pressure rise of dust clouds Kst), EN ISO/IEC 80079-20-2 and with the option of testing to ASTM E1226. Explosive atmosphere is produced by injecting the sample under test through a spherical nozzle. The flammable dust is placed into a dust agitator having a volume of 5.4 litres, which is pressurized to 20 bar. It is opened using an electro-pneumatic quick release valve. Two pyrotechnic initiators are used, each having a value of 5 kJ, which are placed in the centre of the explosion vessel. The 1m 3 test vessel has a H/D ratio of 1,15, static pressure resistance of 16 bar and maximum dynamic test pressure of 23 bar. The ST class is based on the Kst value as follows: ST class 0 - Kst value = 0 ST class 1 - Kst value less than 200 bar m/sec ST class 2 - Kst value between 200 and 300 bar m/sec ST class 3 - Kst value greater than 300 bar m/sec



















