Explosion Testing for dust, gases & vapours


© January 2026
Explosion indices test (K
st
value and P
max
)
Dust explosion classes ST1, ST2 & ST3
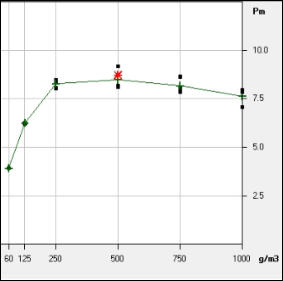
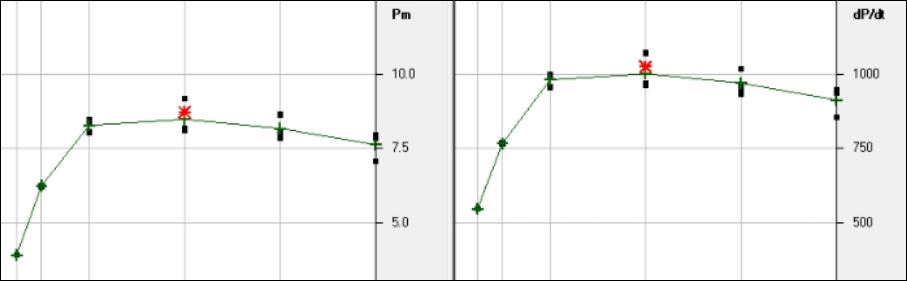
Kst value and Pmax are explosive properties measured in the laboratory to quantify the severity of a dust explosion. The explosion indices test follows EN 14034-1:2004 (determination of the maximum explosion pressure Pmax of dust clouds) and EN 14034-2:2006 (determination of the maximum rate of explosion pressure rise of dust clouds Kst). The tests are carried out in a 20 litre sphere apparatus which reproduces a high state of turbulence to simulate worst case process plant conditions. A weighed quantity of combustible dust is placed into the dust container. The main explosion chamber is then evacuated to 0.4 bar absolute. An automatic test sequence is initiated to pressurise the dust container to 20 bar gauge, and then the fast acting valve on the dust container outlet is opened to allow material into the explosion chamber. The rebound nozzle ensures an even distribution of dust within the explosion chamber and the control system activates two 5 KJ chemical igniters at the centre of the sphere 60 ms after the dust has been dispersed. Explosion pressures are measured for a range of dust concentrations using piezo-electric pressure transducers. The tests are carried out over three series to ensure a thorough investigation of the explosion properties. From the tests, the arithmetic mean of the maximum values (both maximum pressure and maximum rate of pressure rise) is obtained. The Kst value is calculated as the equivalent pressure in a 1 m 3 sphere from the cube law (Kst value = cube root of volume x explosion pressure rise). The ST class is based on the Kst value as follows: ST class 0 - Kst value = 0 ST class 1 - Kst value less than 200 bar m/sec ST class 2 - Kst value between 200 and 300 bar m/sec ST class 3 - Kst value greater than 300 bar m/sec Explosion testing for Kst value & Pmax is essential to validate protection design (explosion venting, explosion suppression and explosion containment). Results of testing from our database for common dusts are shown in the table below.
Kst, Pmax & ST class test results table


Material
Kst
Pmax
ST class
Grain dust
89bar.m/sec
9.3bar g
ST1
Coal dust
85bar.m/sec
6.4bar g
ST1
Flour
63bar.m/sec
9.7bar g
ST1
Sugar
138bar.m/sec
8.5bar g
ST1
Wood dust
224bar.m/sec
10.3bar g
ST2
Aluminium dust
515bar.m/sec
11.2bar g
ST3
Sewage sludge
102bar.m/sec
8.1bar g
ST1
GRP dust
216bar.m/sec
7.6bar g
ST2


- Classification test
- Explosion indices test
- 1m3 explosion test
- Minimum ignition energy
- Minimum ignition temperature
- Layer ignition temperature
- Limiting oxygen concentration
- Lower explosible limit
- Isothermal basket test
- Powder volume resistivity
- Train fire
- Thermal screen
- Air Over Layer
- UN Classification testing
Explosion Testing


© January 2026
Explosion indices
test
(K
st
value and P
max
)
Dust explosion classes
ST1, ST2 & ST3
Kst value and Pmax are explosive properties measured in the laboratory to quantify the severity of a dust explosion. The explosion indices test follows EN 14034-1:2004 (determination of the maximum explosion pressure Pmax of dust clouds) and EN 14034-2:2006 (determination of the maximum rate of explosion pressure rise of dust clouds Kst). The tests are carried out in a 20 litre sphere apparatus which reproduces a high state of turbulence to simulate worst case process plant conditions. A weighed quantity of combustible dust is placed into the dust container. The main explosion chamber is then evacuated to 0.4 bar absolute. An automatic test sequence is initiated to pressurise the dust container to 20 bar gauge, and then the fast acting valve on the dust container outlet is opened to allow material into the explosion chamber. The rebound nozzle ensures an even distribution of dust within the explosion chamber and the control system activates two 5 KJ chemical igniters at the centre of the sphere 60 ms after the dust has been dispersed. Explosion pressures are measured for a range of dust concentrations using piezo- electric pressure transducers. The tests are carried out over three series to ensure a thorough investigation of the explosion properties. From the tests, the arithmetic mean of the maximum values (both maximum pressure and maximum rate of pressure rise) is obtained. The Kst value is calculated as the equivalent pressure in a 1 m 3 sphere from the cube law (Kst value = cube root of volume x explosion pressure rise). The ST class is based on the Kst value as follows: ST class 0 - Kst value = 0 ST class 1 - Kst value less than 200 bar m/sec ST class 2 - Kst value between 200 and 300 bar m/sec ST class 3 - Kst value greater than 300 bar m/sec Explosion testing for Kst value & Pmax is essential to validate protection design (explosion venting, explosion suppression and explosion containment).